I have probably received more requests for our glucose gel protocol than any other question since I started writing on this blog. Dextrose gel has been used more and more often for treatment of hypoglycemia such that it is now a key strategy in the management of low blood sugar in ours and many other institutions. If you are interested in the past analyses of the supporting trials they can be found in these posts; Glucose gel For Managing Hypoglycemia. Can We Afford Not To Use It? and Dextrose gel for hypoglycemia: Safe in the long run? As you can tell from these posts I am a fan of dextrose gel and eagerly await our own analysis of the impact of using gel on NICU admission rates for one!
But What If You Could Prevent Hypoglycemia Rather Than Treating It?
This is the question that the same group who has conducted the other trials sought to answer in their dose finding study entitled Prophylactic Oral Dextrose Gel for Newborn Babies at Risk of Neonatal Hypoglycaemia: A Randomised Controlled Dose-Finding Trial (the Pre-hPOD Study). I suppose it was only a matter of time that someone asked the question; “What if we prophylactically gave at risk babies dextrose gel? Could we prevent them from becoming hypoglycemic and reduce admissions and improve breastfeeding rates as has been seen with treatment of established hypoglycemia?” That is what they went out and did. The group selected at risk patients such as those born to mothers with any type of diabetes, late preterm infants, SGA and others typically classified as being at risk but who did not require NICU admission at 1 hour of age when treatment was provided. The primary outcome was hypoglcyemia (<2.6 mmol/L) in the first 48 hours. Secondary outcomes included NICU admissions, breastfeeding rates in hospital and after discharge as well as formula intake at various time points.
The study sought really to serve as a pilot whose goal was to determine when compared to placebo whether several different regimens could prevent development of hypoglycemia. The groups were (with the first dose in each case given at 1 hour of age):
- Single dose of 40% dextrose gel – 0.5 mL/kg
- Single dose of 40% dextrose gel – 1 ml/kg
- Four doses of 0.5 mL/kg given every three hours with breastfeeding
- A single dose of 1 mL/kg then 3 X 0.5 mL/kg given q3h before each breastfeed.
In total 412 patients were randomized into 8 different groups (4 treatment and 4 placebo).
As The Saying Goes, Less Is More
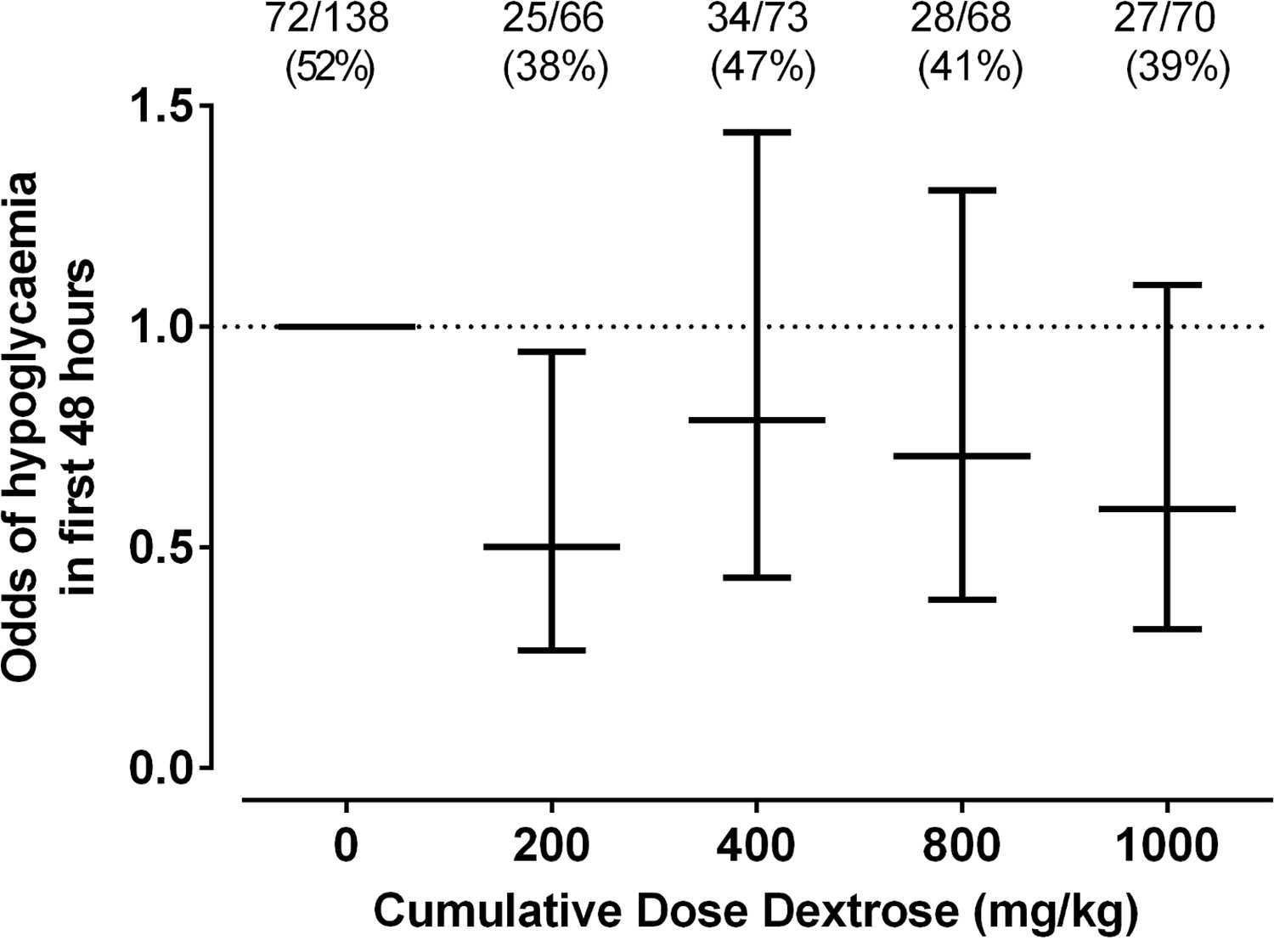
The only dose of dextrose that reduced the risk of hypoglycemia in the first 48 hours was 0.5 mL/kg which provides 200 mg/kg of dextrose which is the same as a bolus of IV dextrose when giving 2 mL/kg of D10W. Curiously using a higher dose or using multiple doses had no effect on reducing the risk. Based on a difference of 14% between placebo and this group you would need to treat roughly 7 patients with dextrose gel once to prevent one episode of hypoglycemia. Also worth noting is that admission to NICU was no different but if one restricted the reason for admission to hypoglycemia the difference was significant (13% vs 2% risk; p = 0.04). What was not seen here was a difference in rates of breastfeeding and much effect on use of formula.
Why Might These Results Have Occurred?
Insulin levels were not measured in this study but I truly wonder if the reason for hypoglycemia in the other groups may have been transient hyperinsulinemia from essentially receiving either a very large load of glucose (1 mL/kg groups) or effectively 4 boluses of glucose in the first 12 hours of feeding. Rebound hypoglycemia from IV boluses is a known phenomenon as insulin levels surge to deal with the large dextrose load and I can’t help but wonder if that is the reason that all but the single dose regimen had an effect. It is also worth commenting that with so many secondary outcomes in this study the p values needed to reach significance are likely much smaller than 0.05 so I would take the reduction in NICU admissions for hypoglycemia with a grain of salt although at least the trend is encouraging.
I wouldn’t change my practice yet and the authors do acknowledge in the article that a much larger study is now being done using the single dose of 0.5 mL/kg to look at outcomes and until that is published I don’t think a practice change is in order. What this study does reinforce though is that providing multiple doses of dextrose gel may yield diminishing returns. While the goal here was prophylaxis, I can’t help but think about the patients who are symptomatic and receive two or three gels and still wind up with an IV. Could it be the same rebound hypoglycemia at play?
We also have to acknowledge that even if this is an effective preventative strategy, is it in the best interests of the babies to all receive such treatment when at least in 6 babies they wouldn’t have needed any? Could such treatment simply be reserved as has been done for those who develop hypoglycemia? Those who question the safety of the ingredients such as dyes that are found in the product may want some long term safety data before this becomes routine in at risk babies but it won’t surprise me if such strategies become commonplace pending the results of the larger trial on the way.

Interesting
We started using the gel at the first of the year; we’re looking at our data now, so will check back in with the group to see how others are doing. No side effects noted, it’s messy, but breastfeeding is still going well. Key thing is to be sure staff understand the importance of buccal administration. Is anyone working on a neonatal product? Maybe denser and without flavoring?